Brain-inspired Neural Circuit Evolution Empowers Spiking Neural Networks
Font:【B】 【M】 【S】
Recently, the Brain-Inspired Cognitive AI team led by Researcher Zeng Yi of the Laboratory of Brain Atlas and Brain-inspired Intelligence, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, published a new study titled Brain-inspired neural circuit evolution for spiking neural networks in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). Inspired by the diversity of biological brain circuits shaped by natural evolution and spike-timing-dependent plasticity mechanisms, they proposed a brain-inspired neural circuit evolution strategy to help develop spiking neural networks with greater biological plausibility and efficiency.
In biological neural systems, different types of neurons self-organize into diverse connectivity patterns to structurally support rich cognitive functions. Different neural circuits in the human brain and their adaptive capabilities enable perception, learning, decision-making, and other higher cognitive functions. However, current design paradigms for spiking neural networks (SNNs) are mostly inspired by structures in deep learning, which are dominated by feedforward connections and ignore the diversity of neuron types, significantly limiting SNNs’ potential on complex tasks. From a computational perspective, uncovering the rich dynamical properties of biological neural circuits and applying these insights to the structure of brain-inspired SNNs remains a profound and open challenge.
Zeng Yi’s team designed an evolutionary modeling framework that combines feedforward and feedback connections with excitatory and inhibitory neurons to provide a more biologically plausible evolutionary space for intelligent computation. By leveraging local spike behavior of neurons and local rules of spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP), the model adaptively evolves functionally meaningful neural circuits similar to those generated through natural evolution, such as feedforward excitation, feedforward inhibition, feedback inhibition, and lateral inhibition, while globally updating synaptic weights using error signals. By incorporating these evolved circuits, the study built brain-inspired SNNs for image classification as well as reinforcement learning and decision-making tasks. Using this brain-inspired neural circuit evolution strategy (NeuEvo) and its evolved repertoire of circuit types, the resulting SNNs achieved greatly enhanced perception, reinforcement learning, and decision-making capabilities.
NeuEvo achieved state-of-the-art performance at submission time on datasets including CIFAR10, DVS-CIFAR10, DVS-Gesture, and N-Caltech101, and achieved representative accuracy for SNNs on ImageNet. Combined with online and offline deep reinforcement learning algorithms, it achieved performance comparable to artificial neural networks. The evolved brain-inspired neural circuits lay the foundation for the evolution of networks with complex functions and the emergence of cognitive abilities.
Researcher Zeng Yi commented:
"Our team has long focused on brain-inspired cognitive intelligence, whose theoretical foundation is our brain-inspired plasticity framework — also the theoretical core of the BrainCog brain-inspired cognitive intelligence engine that we have developed and released. This framework features multi-scale and multi-dimensional aspects: in spatial scale, from ion-channel interactions at the micro-scale to neuron-to-neuron interactions at the meso-scale and coordinated brain regions at the macro-scale; in temporal scale, it involves the coordination of learning, development, and evolution. The deep integration of temporal and spatial scales shapes the low-power, high-performance, highly intelligent properties of biological brains and brain-inspired AI. In recent years, our team has made a series of advances and insights in integrating learning, development, and evolution. This study helps us further improve that framework. Through computational modeling, we simulate the 'use it or lose it' principle observed in natural structural evolution, autonomously evolving a rich variety of neural circuit types. The most interesting part is that these types of circuits also exist in real biological brains. Our experiments show these structures can better address core problems in learning and decision-making — 'what exists in nature makes sense' — offering endless inspiration for future research into general brain-inspired cognitive intelligence."
PhD student Shen Guobin and Assistant Researcher Zhao Dongcheng of the Laboratory of Brain Atlas and Brain-inspired Intelligence are co-first authors of this paper. Researcher Zeng Yi is the corresponding author. PhD student Dong Yiting is a co-author.
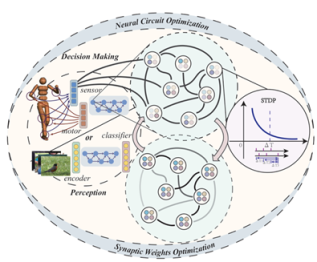
Evolution of brain-inspired neural circuits for SNNs
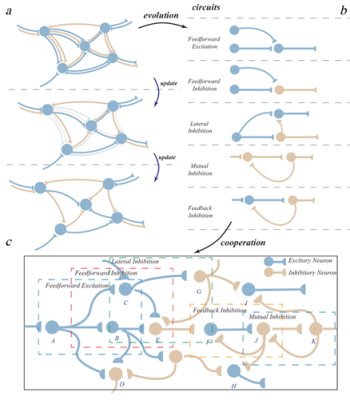
A. Evolution process of neural circuit structures. B. Diagram of different neural circuits. C. Examples of complex circuits obtained by NeuEvo.
Paper link: https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2218173120
Copyright Institute of Automation Chinese Academy of Sciences All Rights Reserved
Address: 95 Zhongguancun East Road, 100190, BEIJING, CHINA
Email:brain-ai@ia.ac.cn